The carbon footprint in construction refers to the total amount of greenhouse gases emitted throughout a project’s entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction to building demolition. It is typically divided into two main categories: embodied carbon (from materials and construction processes) and operational carbon (from the building’s energy use).
With the growing global commitment to sustainability, the construction industry is at a crucial turning point in adopting more environmentally responsible practices. Therefore, our team at personalHOME adopts the following strategies to reduce the carbon footprint:
1. Material Selection
Choosing sustainable materials represents one of the most impactful decisions in reducing the carbon footprint. Local materials minimize transportation emissions, while options like bamboo, certified wood, recycled concrete, and compressed earth blocks offer alternatives with a lower environmental impact.
2. Bioclimatic Design and Energy Efficiency
Bioclimatic design leverages local climate conditions to optimize indoor comfort and reduce energy consumption. This includes strategic building orientation, maximizing natural light, cross-ventilation, and using thermal mass to regulate temperature.
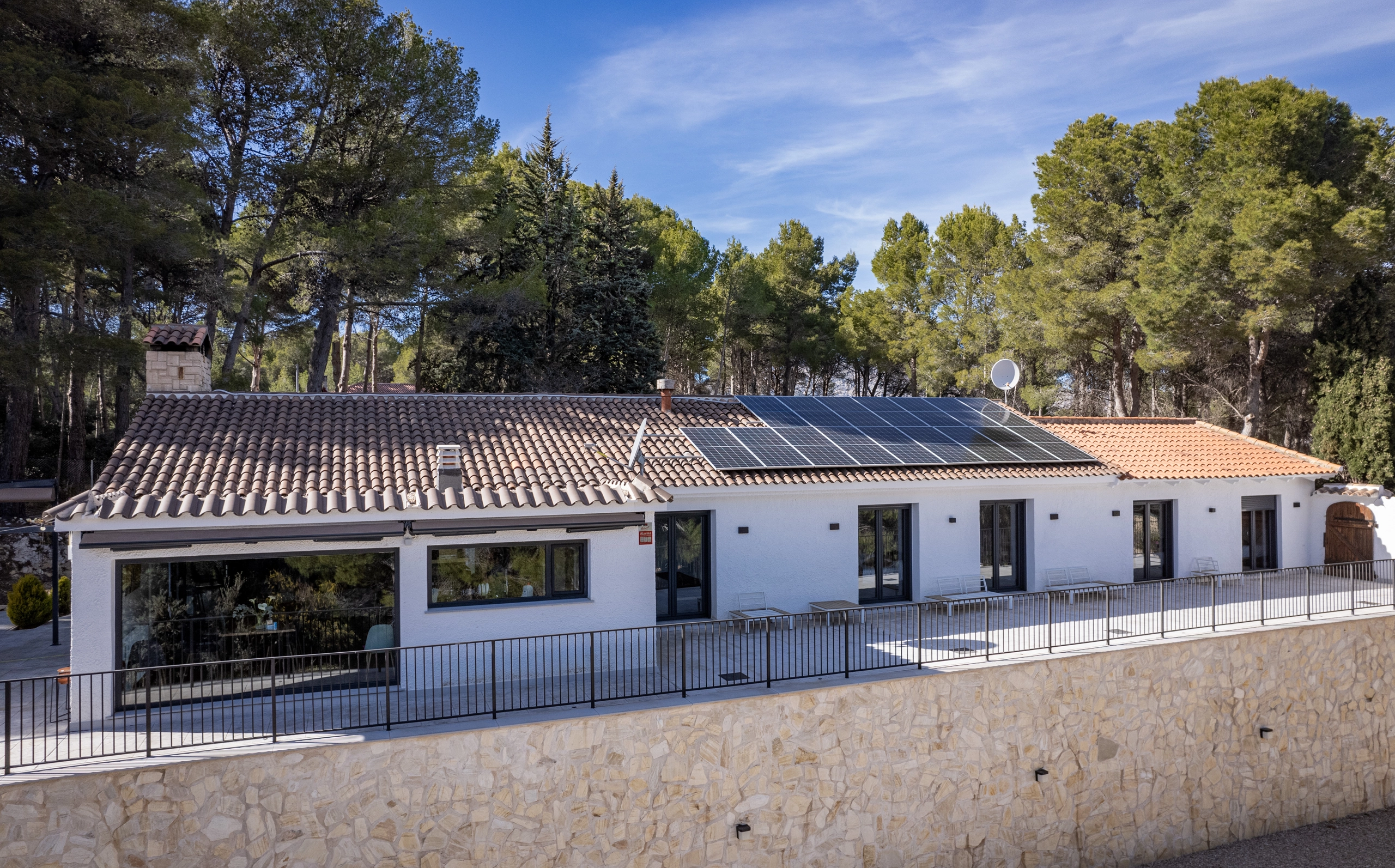
3. Integration of Renewable Energies
Incorporating solar panels, geothermal, and aerothermal systems, small wind turbines, and solar water heating systems allows buildings to generate their own clean energy. These systems, combined with battery storage, can move buildings towards energy neutrality or even turn them into net energy generators.
4. Efficient Water Management
Rainwater harvesting and reuse systems, on-site greywater treatment, and the implementation of low-water consumption technologies reduce both environmental impact and operational costs. Rain gardens and permeable surfaces also contribute to sustainable water management on site.
5. Modular and Prefabricated Construction
Modular and prefabricated construction allows for better quality control, reduces material waste, and optimizes construction processes. This methodology can reduce construction times by up to 50% and minimize emissions associated with transporting heavy machinery to the site.
6. On-Site Waste Management
Implementing waste management plans that include source separation, material reuse, and recycling can significantly reduce construction’s environmental impact. Precise planning and the use of technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM) help minimize waste from the design phase to project completion.
Despite the clear benefits, adopting sustainable practices in construction faces challenges such as higher initial costs, a lack of specialized training, and resistance to change within the industry. However, these obstacles are gradually being overcome as technology becomes more accessible, long-term economic benefits become clearer, and environmental regulations tighten.